 |
Science Frontiers ONLINE No. 43: Jan-Feb 1986 |
|
|
Treasures In A Toxonomic Wastebasket
The Burgess Shale, in British Columbia, ia all that is left of a Middle Cambrian mudbank that adjoined a massive algal reef. Here, many "experimental" forms of life prospered and succumbed. The Burgess Shale is probably the world's greatest depository of fossils of softbodied creatures. Quoting Stephen Jay Gould:
"The Burgess (fortunately for us) occupies a crucial time in life's history. It represents our only 'window' upon the first great radiation of complex life on earth. All but one or two modern phyla originated in a burst of evolutionary activity associated with the so-called Cambrian explosion some 570 million years ago. The Burgess provides our only peek at the soft-bodied forms of this first flowering. All other soft-bodied fossil assemblages are much younger; they represent faunas well past the initial burst and sorting out of Cambrian times."
The morphological diversity of the Burgess Shale, incorporating many bizarre forms of life, represents a true biological revolution. Here are found a dozen genera that do not fit into any modern phylum. Most of the novelties never survived into modern times.
(Gould, Stephen Jay; "Treasures in a Taxonomic Wastebasket," Natural History, 94:24, December 1985.)
Comment. Somewhere on today's earth, there must be mudbanks washed by nutrient-rich waters and bathed in tropical sunlight. Is some ingredient missing, or perhaps present, in today's mudbands that suppresses the wild speciation seen in the Burgess Shale?
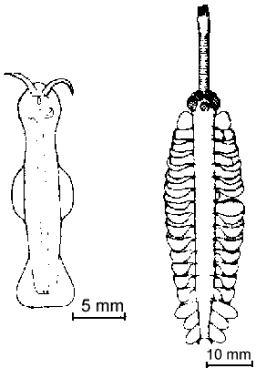 | Tow of the many mysterous fossils found in Burgess shale. At the right is Opabina regalis, with five eyes at the base of a nose-like structure ending in teeth. On the left is Amiskwia sagittoformis. Although these creatures are named, nobody really knows what they are! |