 |
Science Frontiers ONLINE No. 65: Sep-Oct 1989 |
|
|
Microorganisms At Great Depths
It was a surprise when diverse biological communities were discovered around deep-sea thermal vents, where sunlight is nonexistent and the energy for sustaining life must be extracted from the mineral-charged water gushing from the vents. An analogous situation occurs at great depths in the earth's crust itself, as proven by sampling at three deep boreholes in South Carolina.
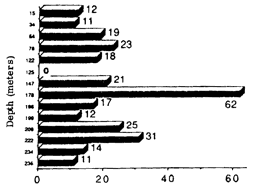 Number of microorganism colony types at various depths at Site P28. |
As the following two paragraphs demonstrate, subterranean life consists of many well-adapted microorganisms working together.
"The traditional scientific concept of an abiological terrestrial subsurface is not valid. The reported investigation has demonstrated that the terrestrial deep subsurface is a habitat of great biological diversity and activity that does not decrease significantly with increasing depth.
"The enormous diversity of the microbiological communities in deep terrestrial sediments is most striking. The organisms vary widely in structure and function, and they are capable of transforming a variety of organic and inorganic compounds. Regardless of the depth sampled, the microorganisms were able to perform the cycling of carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, manganese, iron, and phosphorous. Although the organisms were not of the same physiological types, each niche contained a basic cast of microbiological players capable of these nutrient transformations. Such versatility is surprising, and contrary to traditional thinking in soil microbiology, because the deep subsurface is presumably a nutrientlimited environment where photosynthesis and photosynthates are not abundant."
The scientists writing this article speculate that similar microorganisms could well be prospering far below the Martian surface, where they are sheltered from radiation and the cruel surface environment.
(Fliermans, Carl B., and Balkwill, David L.; "Microbial Life in Deep Terrestrial Subsurfaces," Bio Science, 39: 370, 1989.)