 |
Science Frontiers ONLINE No. 75: May-Jun 1991 |
|
|
Of iron whiskers and particles that increase mass with age!
Two pillars of the Big Bang hypothesis are: (1) Redshifts of galaxies support the notion of an expanding universe; and (2) The background microwave radiation can be interpreted as the dying embers of the Big Bang itself. Proponents of the Big Bang feel secure atop these pillars. But should they?
A few Big-Bang skeptics, who have survived considerable establishment pressure, see growing cracks in those pillars. J. Narlikar identified two such cracks and, best of all, offered exciting remedies: (1) The redshift relationship, which works well with galaxies, falls apart when applied to quasars (see graphs); and (2) The background microwave radiation is much too smooth to come from the lumpy universe we observe. Narlikar opines as follows:
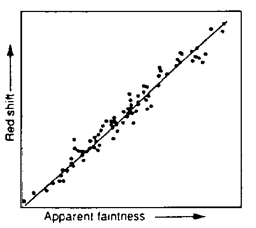 Plot of red shift versus galaxy faintness supports the proposition that red shift is proportional to distance |
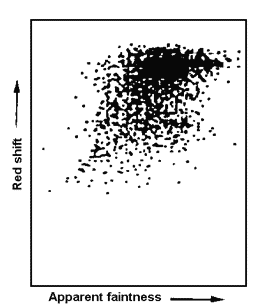 The same plot for quasars produces a scatter of points, suggesting that here red shifts have nothing to do with distance. |
"Given these problems, it is not a sound strategy to put all of our cosmic eggs in one big-bang basket. Rather, we should explore other possibilities. Thirty years ago, there was a more open debate on alternative theories, which made valuable contributions to our undersanding of cosmology. For a healthy growth of the subject, the big bang hypothesis needs competition from other ideas."
Some of Narlikar's suggestions are heresies of the first order:
- Particles are born with zero mass and acquire mass only as they interact with other matter in the universe (consistent with Mach's principle). The radiation from the lighter particles making up young quasars would thus be redshifted when compared to radiation from old galaxies.
- The background microwave radiation from a lumpy universe could easily be smoothed out by tiny (1 mm) iron whiskers condensing in the expanding envelopes of supernovae.
Comment. These ideas are almost as audacious as the suggestion that continents can actually drift apart! But are they enough to lift the intellectual pall created by a hypothesis-enshrined-as-fact?
Reference. The Big Bang paradigm is challenged repeatedly in chapters ATR and AWB in our catalog: Stars Galaxies, Cosmos. Details here.