 |
Science Frontiers ONLINE No. 87: May-Jun 1993 |
|
|
Fossil Feathers Fly
 A. Feduccia's cartoon of the bug-catching phase of bird evolution |
The scientific acrimony centers on whether this ancient bird really evolved from small theropod dinosaurs. Prevailing theory has it that these dinosaurs first evolved feathers to keep warm and then used their feathered "arms" to help capture insects, and so on, with some aimless flapping, to the attainment of true flight. A rival, officially frownedupon theory has it that birds evolved from tree-dwelling reptiles that evolved feathers to break their falls while jumping from branch to branch! [Somehow, neither theory strikes a realistic chord. Why couldn't feathers have evolved solely for the purpose of flight? Answer: because evolutionists cannot countenance purpose in nature. WRC]
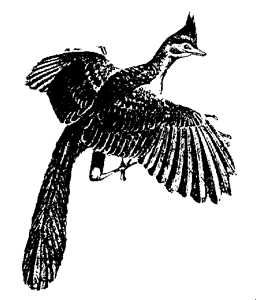 One reconstruction of Archaeopteryx. There is a remarkable superficial resemblance to the living South American hoatzin. Young hoatzin even sport claws on their wings. |
(Feduccia, Alan; "Evidence from Claw Geometry Indicating Arboreal Habits of Archaeopteryx," Science, 259:790, 1993. Morell, Virginia; "Archaeopteryx: Early Bird Catches a Can of Worms," Science, 259:764, 1993. Monastersky, R.; "Flight: A Bird Hand Is Worthy in the Bush," Science News, 143:87, 1993.)
Comment. Unremarked in the three articles referenced above is a more serious anomaly that is highlighted by the many modern features of Archaeopteryx; for example, the lack of any transitional fossils between Archaeopteryx and its ancestors. Where are reptiles with crudely feathered, but somehow useful tails?