 |
Science Frontiers ONLINE No. 90: Nov-Dec 1993 |
|
|
A Tale Of Two Noses
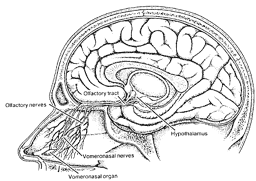 The vomeronasal and olfactory sensory systems. (L. Stansass, M. Reingold) |
Next: A Look Up the Nose. Biologists have long realized that animal noses actually contain two sensory channels. The first is the familiar olfactory system, which humans also possess. The second channel is the vomeronasal system. In animals, each system has its own separate organs, nerves, and bumps in the brain. The function of the vomeronasal system is pheromone detection. It was widely believed that humans had long ago discarded this sensory system along evolution's trail. But a closer look at the human nose by B. Jafek and D. Moran, affiliated with the Rocky Mountain Taste and Smell Center at the University of Colorado, revealed that all humans examined displayed two tiny pits on both sides of the septum, just inside the the opening of the nose. Behind the holes were tubes lined with unique cells that could well be pheromone detectors, since they responded positively to puffs of air laden with pheromones.
In conclusion, we humans actually do have a sixth sense, and we are all enveloped in an aura -- not the luminous aura of the mystics but a cloud of pheromones. Somehow, our attitudes towards others are likely affected by these pheromones. (Blakeslee, Sandra; "Human Nose May Hold an Additional Organ for a Real Sixth Sense," New York Times, September 7, 1993. Cr. P. Gunkel)