 |
Science Frontiers ONLINE No. 137: SEP-OCT 2001 |
|
|
Granite-working In Ancient Egypt
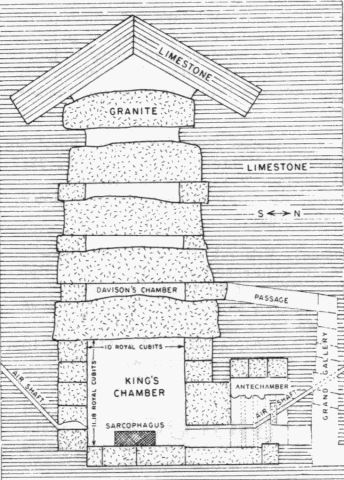 The King's Chamber in the Great Pyramid is encased with multiton blocks of hard-to-work granite. For some reason the five granite slabs in the ceiling were finished on only their bottom sides. (From: Ancient Structures) |
As a matter of fact, there is little mystery here despite what you read in the popular magazines. The Egyptian workers simply dribbled quartz sand beneath the copper saws and drills. This abrasive is harder than the mica and feldspar components of granite but not the quartz. Nevertheless, granite will yield slowly to the abrasive, as do the copper tools themselves.
In 1999, D.A. Stocks tested the efficacy of copper saws and drills on the granite in the Aswan quarries 500 miles up the Nile. The copper saw in his test was 1.8 meters long, 15 centimeters in depth, and 6 millimeters thick. Stocks experimented with both wet and dry sand and smooth and notched saws. In one test, workmen cut a slot 3 centimeters deep and 95 centimeters long in14 hours. It was slow work, but the ancient Egyptians had plenty of time and manpower. In the same experiment, the copper saw blade was ground down 7.5 millimeters. Overall, dry sand with a smooth blade worked best.
Similar tests with a tubular copper drill were also successful.
(Stocks, Denys A.; "Testing Ancient Egyptian Granite-Working Methods in Aswan, Upper Egypt," Antiquity, 75:89, 2001.)
Comment. Stocks did not confront a potential stone-working anomaly identified by C. Dunn in his The Giza Pyramid. It seems that the drill marks on the sides of the sarcophagus in the King's Chamber imply that the soft copper Egyptian drills apparently advanced about 500 times faster than possible with the toughest modern drills! There is something amiss here.
Other Sites of Interest
|